What Are Enneagram Triads?
The Enneagram is a unique analytic system that uses numbers One to Nine to represent and explain the spectrum of personality types. A means to explore and understand your personality type, the enneagram explains how people behave based on the number in which their dominant trait falls in. The enneagram triad system comprises nine personality types.
Don Riso and Russ Hudson grouped these types into three centers. The centers form the Enneagram triads. A person may belong to more than one of the enneagram types.
We can use the enneagram as a tool to help us understand ourselves better and improve our relationships with other people. Perhaps because it uses numbers, the system may appear complicated, but it is quite simple if you take it one step at a time.
The credit for the original system goes to Oscar Ichazo. Don Riso developed the original 9-sided enneagram personality system in 1977. He outlined the traits that made up each type. In the 1990s, Don Riso and Russ Hudson worked together to improve the system further. They included the enneagram levels of development at this time.
The Enneagram Triads Diagram
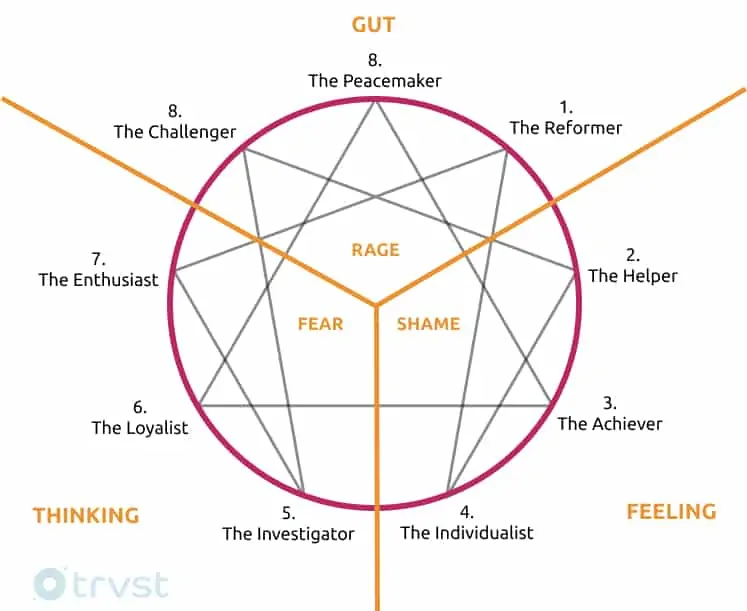
You can begin your journey to understanding the system using enneagram diagrams. If you can not find one readily, you can sketch it out yourself. The diagram consists of a circle, large enough to have nine numbers placed around its circumference, like a clock. The numbers are from 1 to 9. Each number represents one of the types of personality.
Inside the circle, the numbers connect by some lines. Numbers 6, 3, and 9 connect to form a triangle; however, the other lines’ shape is irregular. Number 1 connects to numbers 7 and 4, while number 7 also connects with number 5, and number 4 connects with number 2. Number 8 connects with numbers 5 and 2.
So, each number connects directly to two numbers. The connection between the numbers shows the relationship between personality types. This indicates that although you might have a dominant center or personality type, you can possess other personality types. The types connect with wings, arrows, and triads.
The Wings
The wing of a type is either one of the two types adjacent to it. Your basic type dominates your personality and points you to which of the triads you belong to. But your wing is your alter ego. It is what complements or contradicts your basic personality.
When you find yourself acting in a way you usually wouldn't, you are most likely operating on your wing type. Since each type’s wing is one of the types next to it on both sides, your wing may belong to another triad. For example, if you are a type Two, you can have a One-wing or a Three-wing. Some observations reveal that some people may have both wings, but one dominates the other.
To make your personalized enneagram chart, you can take the Riso- Hudson Enneagram Type Indicator test to determine your basic personality type. Then, you will know which of the triads you belong to. With careful consideration, you can pick out the enneagram wing that is yours.
The Nine Enneagram Personality Types
Type 1- The Reformer
A reformer is purpose-driven, principled, and has firm self-control, especially when it comes to angry feelings. A reformer aspires for perfection in all things. The reformer is idealistic with a rigid sense of right and wrong. Wherever they find themselves, reformers always try to improve the situation. They are fearful of making mistakes and can be critical of others. They set high standards and are impatient with people who they deem lackadaisical.
Type 2- The Helper:
A person who has a helper personality is generous and loves to go to great lengths to make people happy. They are also quite possessive. The helper is caring and places great value on relationships and positive feelings. Helpers are sentimental, friendly, warm, and welcoming. They love being needed by others and can fall into the habit of self-neglect while trying to please people. They suppress negative feelings of anger and resentment to continue feeling like good people.
Type 3- The Achiever
The achiever likes to get things done; They are goal-oriented and image-conscious. An achiever is ambitious, competent, and charismatic. An achiever enjoys being looked up to as a standard of success or professionalism in his field of endeavor. The achievers are self-assured, possess a positive attitude, and continuously measure themselves against others by achievements. Achievers are competitive and can become workaholics in the process of trying to beat the competition. However, they can also find themselves out of touch with their underlying feelings.
Type 4- The Individualist
This personality type values self-expression and is dramatic and temperamental. The individualist is a sensitive, reserved, and self-conscious person. Individualists often have creative and artistic abilities. They are emotionally honest and struggle with feelings of vulnerability and defectiveness. They can be moody and struggle with fitting into the ordinary way of life.
Type 5- The Investigator
This enneagram personality is highly perceptive, curious, and innovative. Investigators have extensive problem-solving skills and a strong sense of independence. They are bold and can come across as very intense people. Sometimes, an investigator may become immersed in his thoughts and isolate himself.
Type 6- The Loyalist
The loyalist type is responsible, reliable, and trustworthy. He is security-conscious and can detect problems at the earliest stages. Loyalists are hardworking and always willing to cooperate with others to achieve common goals. They can get defensive and anxious when stressed. Loyalists are also cautious and indecisive.
Type 7- The Enthusiast
This enneagram type is a thrill-seeker. They are spontaneous, versatile, and acquisitive. The enthusiast is always optimistic, seeking a positive remedy to frustration, and values experience. He is seemingly joyous and appreciative. Enthusiasts typically lack discipline, and this can make them over-extended themselves. They get easily distracted. Enthusiasts are disorganized, impatient, and impulsive.
Type 8- The Challenger
This enneagram type is known to have high levels of self-confidence. A challenger is willful, resourceful, and makes decisions quickly and firmly. They are never shy in the face of a confrontation and may often instigate one. They are honest in a way that people may perceive as harsh and are very protective of the things and people they love. Challengers value power and can be domineering.
Type 9- The Peacemaker
This enneagram type is complacent and resigned. They are also receptive and reassuring. Peacemakers find it easy to trust people and support others. They do not like conflicts and try to overlook or minimize problematic issues. They are easy to be around and don't discriminate against any kind of person. However, they can be extremely stubborn on their bad day or find themselves contending with a feeling of inertia.
The Enneagram Triad
The triads contain three numbers in each of the three center types. The first one is called the feeling center, the second center is the thinking center, and the third center is the instinctive center.
The centers are also called triads. Of the three centers, we deem no one as being better than the others. The triads highlight the dominant emotional trait common with all three types in it. Each of the three types in the center has a different way of reacting to the dominant emotion.
The feeling triad
Enneagram Numbers 2, 3 & 4
People who belong in the Enneagram heart triad, or feeling center, are types Two, Three, and Four. These three types are put together in the heart center because they share common strengths and weaknesses. They desire emotional intimacy.
The heart center’s common attribute is a strong wish to be loved and accepted by the people around them. A common feeling shared by all three types in the feeling triad is shame: somehow, they believe they do not quite measure up to other people. They find it easier to accept themselves when they feel loved and admired by the people around them.
The most powerful emotion in the heart center is the feeling of shame. A person with a type Two personality controls the feeling of shame by getting others to like him. Type Three deals with shame by denying that they feel it. They cope with shame by trying to become successful and valuable.
Type Fours control the feeling of shame by indulging in fantastic imaginations. Those in the heart center also use their creative talents as a way of feeling special.
Finding yourself in the heart center can mean that you connect deeply to your feelings and relate to people based on them. People who belong to the feeling triad can have problems with vulnerability. Because people sometimes misconstrue being emotional as being weak. People associate the heart center with two admirable virtues: empathy and selflessness, often putting the needs of others before their own.
The thinking triad
Enneagram Numbers 5,6 & 7
It is also called the head center and has types Five, Six, and Seven in it. The people who belong to the Enneagram head triad see the world from the perspective of logic. The most powerful emotion in the head triad is fear.
Type Fives cope with the feeling of fear by detaching themselves from the world around them. They feel that they will conquer their fear of the outside world by understanding their complex inner world and may become loners. Type Six has less control over fear and is prone to feelings of anxiety.
People who belong to Enneagram Six may use position, relationships, philosophies, inner knowing, or beliefs to provide them with a sense of security. Type Sevens fear being emotional. Feelings of loss, anxiety, and pain make them uncomfortable. So, they keep their minds occupied with exciting possibilities and engage in stimulating activities to retain the feeling of happiness.
The need for security and comfort motivates people in the head center. When they don't have either of those, they become stressed. They are fond of overthinking and making decisions based on the presence or absence of logic. People in the head center are deep thinkers.
Many associate the head center with wisdom and rationale. Many of those in the thinking triad have reported the benefits of journal writing as a tool to balance their thoughts with the other triads.
The gut triad
Enneagram Numbers 8, 9 & 1
The gut triad is also called the instinctive center or gut center. The three types in it are types Eight, Nine, and One. The dominant emotion in the gut center is anger.
People with type Eight express their anger more forcefully and physically than other types. Type Nines, on the other hand, deal with anger by denying it. They are likely to suppress their feeling of anger because they do not want to make others uncomfortable.
Type Ones try to exercise firm control over their anger. They feel that such control makes them disciplined. Instead of acting out in anger, they will direct the energy into doing something they consider constructive.
People in the gut center like to control the situation of things, directly or indirectly. They make decisions based on strong gut feelings rather than clear thinking. People in this triad have strong intuition and often follow it without much contemplation. They are quick to respond to situations.
Many people in the Enneagram gut triad find mindfulness practice a tool to be in the moment and get in touch with their emotions to achieve balance.
Regardless of which of the enneagram triads you belong to, a more in-depth analysis might show a connection with other center types. We cannot operate in one center without affecting the other two.
Levels of Development

A structure within each type represents the progression of behaviors, attitudes, motivations, and defenses. The development levels explain why two people of the same type may not behave in the same way. The levels represent the degree of intensity at which a specific trait and personal characteristics manifest in a person.
The levels of development are as follows:
Healthy levels
- 1 - Level of Liberation
- 2 - Level of Psychological Capacity
- 3 - Level of Social Value
Average levels
- 4 - Level of Imbalance/ Social Role
- 5 - Level of Interpersonal Control
- 6 - Level of Overcompensation
Unhealthy levels
- 7 - Level of Violation
- 8 - Level of Obsession and Compulsion
- 9 - Level of Pathological Destructiveness
Conclusion
As humans, we are complex and dynamic. While the nine types of enneagram triads may not answer all our questions regarding human behavior, it is an excellent way to explore our personalities. The Enneagram system, triads, and wings help us understand that we can operate in different center types.
With knowledge comes power. You can use the enneagram to become much more self-aware. When you understand your personality and the factors that make you who you are, you can learn to control better how you act. An enneagram is a tool for self-discovery. The nine Enneagram types can help us figure out our strengths and weaknesses.
Jen’s a passionate environmentalist and sustainability expert. With a science degree from Babcock University Jen loves applying her research skills to craft editorial that connects with our global changemaker and readership audiences centered around topics including zero waste, sustainability, climate change, and biodiversity.
Elsewhere Jen’s interests include the role that future technology and data have in helping us solve some of the planet’s biggest challenges.

